Typical metals used in the forging process include carbon, alloy steels, stainless steel and copper alloys. Selecting the appropriate metal ensures that the forged product will meet design specifications and be crafted to the necessary quality. In addition, you want to select a metal that will work for the specific application without experiencing any negative effects such as corrosion, extreme wear and tear, or mechanical failure.
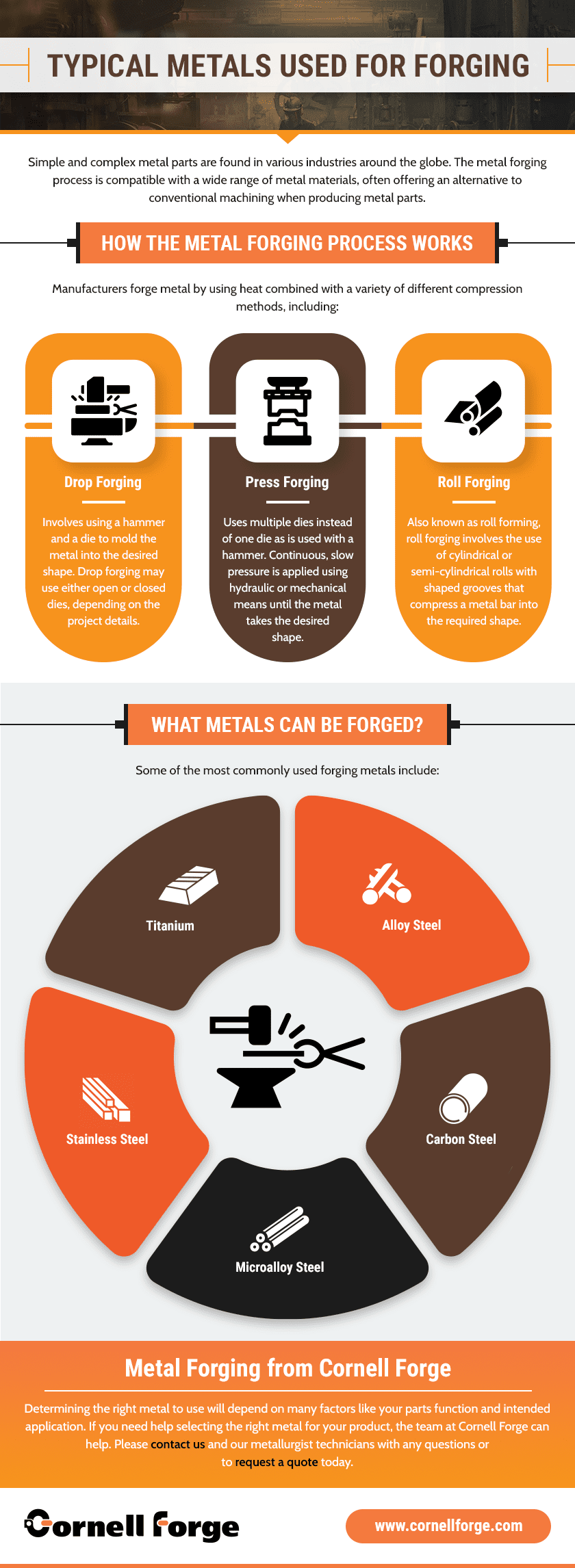
How the Metal Forging Process Works

- Drop forging. Drop forging involves using a hammer and a die to mold the metal into the desired shape. Drop forging may use either open or closed dies, depending on the project details.
- Press forging. Press forging uses multiple dies instead of one die as is used with a hammer. Continuous, slow pressure is applied using hydraulic or mechanical means until the metal takes the desired shape.
- Roll forging. Also known as roll forming, roll forging involves the use of cylindrical or semi-cylindrical rolls with shaped grooves that compress a metal bar into the required shape.
The above methods are often combined with heat to make the metal more ductile. Hot forging allows the manufacturer to change the mechanical and structural properties of the metal to provide certain qualities, such as tensile strength or ductility. This method can also help to further remove impurities in the metal that could cause voids or cracks.
What Metals Can Be Forged?
Determining what metals can be forged will depend largely on the provider that you hire and their production capabilities, though technically, all metals can be forged. Each metal has different properties and reactions when heated or forged using certain methods. Due to these differences, some manufacturers will specialize their processes to work with specific metals, such as steel or titanium.
Here are some common metals used in metal forging.
- Alloy steel. Alloy steel is a broad term referring to a variety of steels that have had their properties altered or enhanced by alloying the steel with additional metals, such as silicon, manganese, or nickel. These added metals may provide specific characteristics such as corrosion resistance, malleability, or thermal/electrical conductivity. Alloy steel offers exceptional wear
resistance and strength for forging metal parts. - Carbon steel. Carbon steel contains higher levels of carbon to offer more increased strength than regular steel. The metal also performs well in high-temperature and high-pressure applications.
- Microalloy steel. Microalloy typically contains additives of vanadium, titanium, or niobium. Microalloy steel develops excellent toughness as it cools, and typically does not require post heat treat to achieve increased mechanical properties.
- Stainless Steel. Stainless steel has exceptional corrosion resistance, heat resistance, strength, and durability. All of these properties get further enhanced when the metal undergoes a forging process.
- Titanium. Titanium is a lightweight metal with exceptional strength. The metal offers superior resistances to corrosion and high temperatures.
Metal Forging from Cornell Forge
Deciding on the right metal to use will depend on your part and how it will function in its intended application. If you need help selecting the right metal for your product, the team at Cornell Forge can help. Our metallurgist and technicians are knowledgeable regarding available forging techniques and how each method will interact with specific metal materials. Please contact us with any questions or request a quote today.